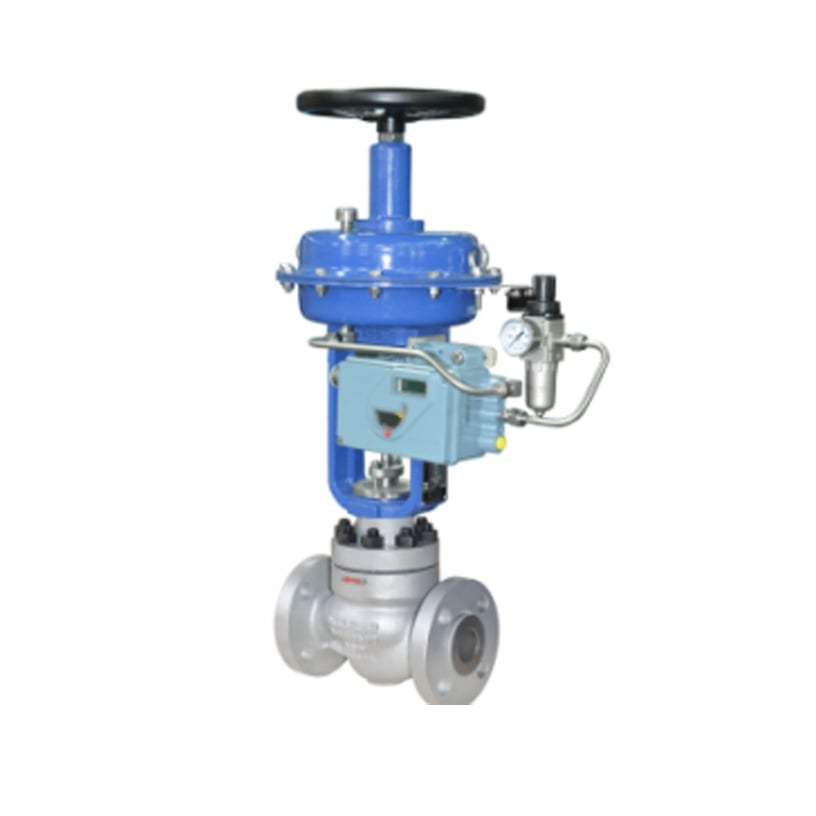
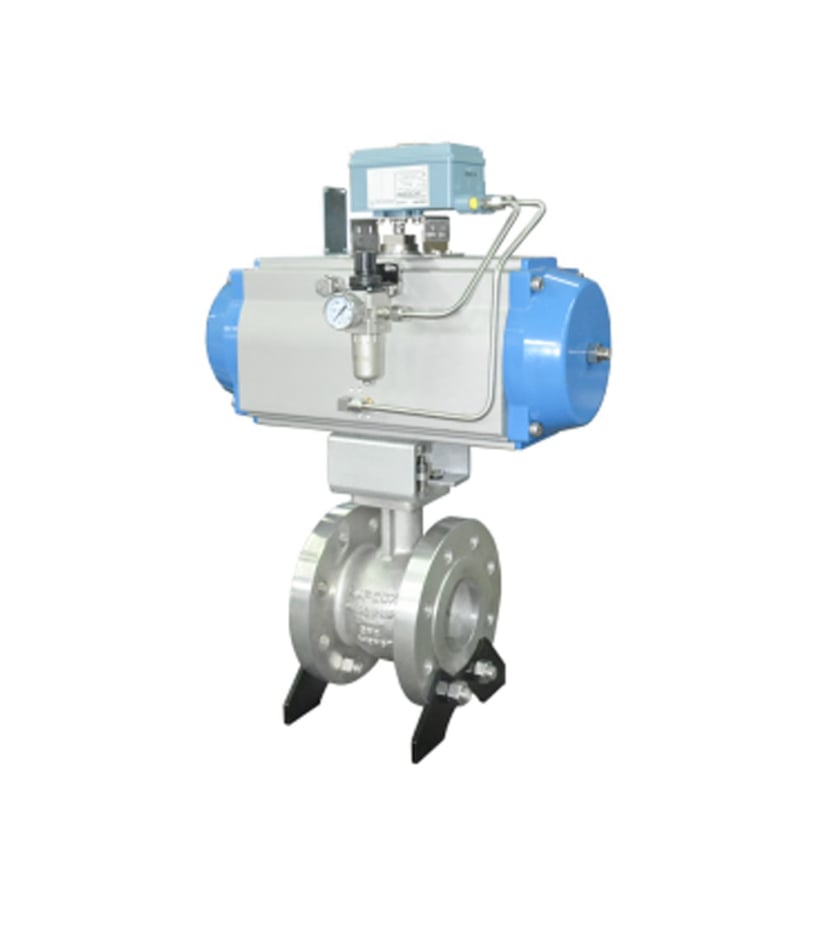
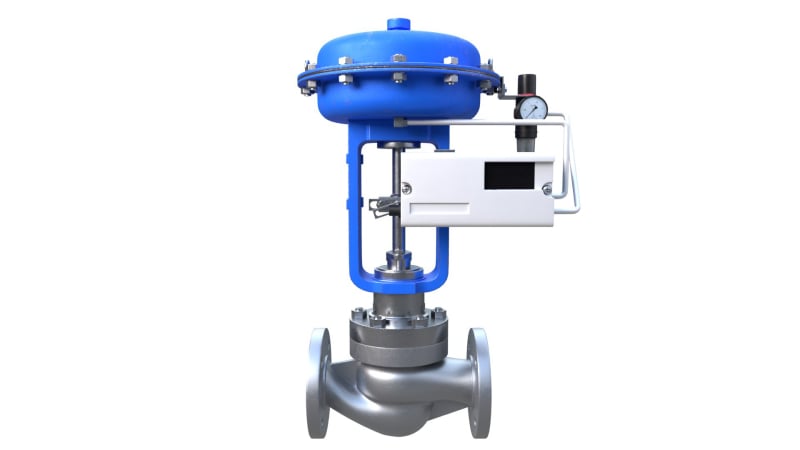
Main Parts of Control Valve

Valve Body
The casing that holds the internal parts.
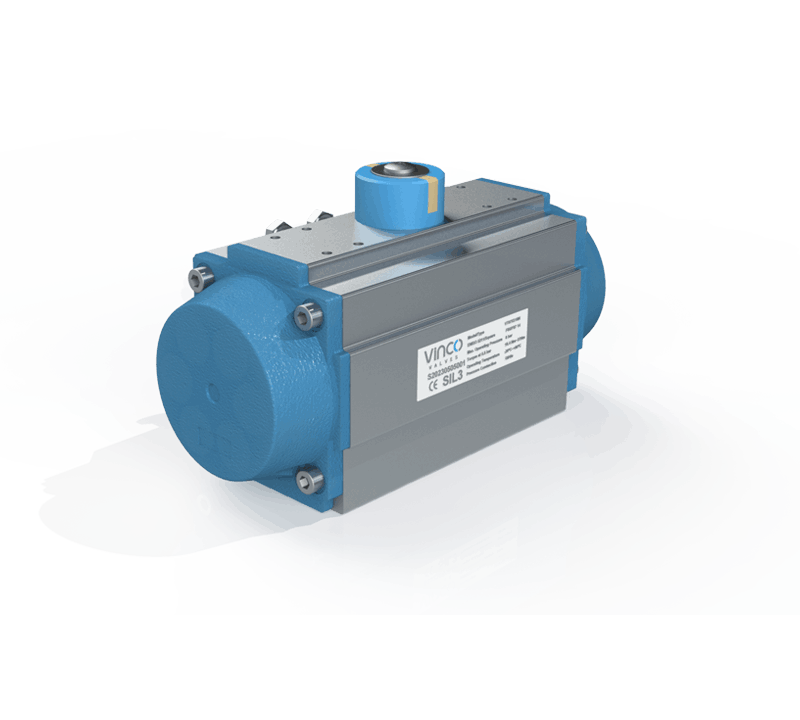
Actuator
The device that moves the valve plug/disc (can be pneumatic, hydraulic, or electric).

Positioner
Ensures the valve opens to the exact position according to the control signal.
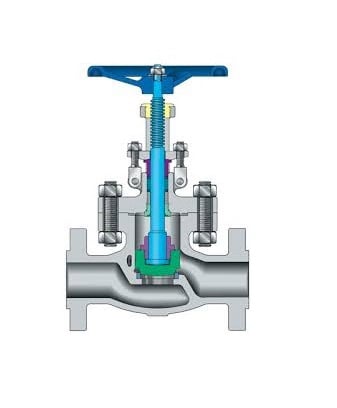
Plug/Disc
Controls the flow by moving up/down or rotating.