Type of Valves
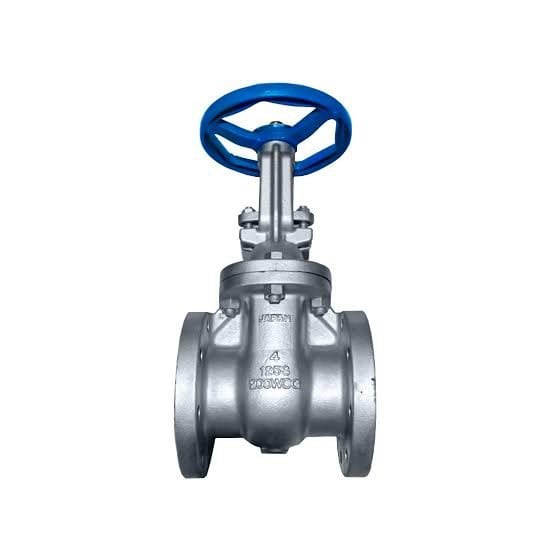

Gate Valve
Function: Used for on/off control (fully open or fully closed).
Has a sliding gate (wedge) that blocks or allows flow.
Not suitable for throttling.
Common in water supply, oil, and gas pipelines.
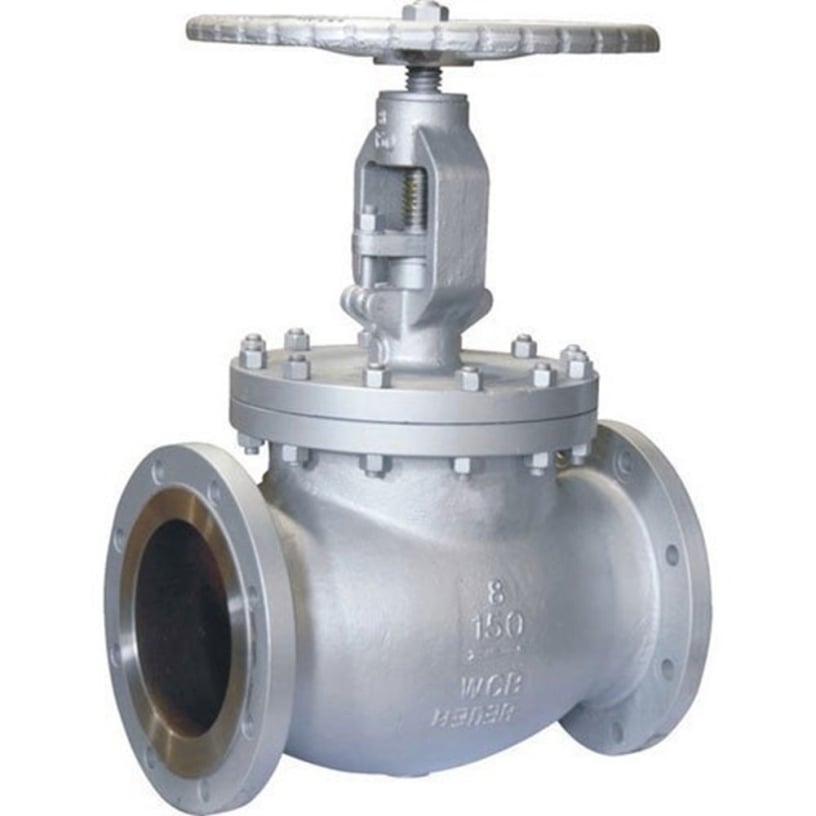

Globe Valve
Function: Used for throttling (flow regulation) and shutoff.
Has a disk that moves up and down against the flow.
Higher pressure drop compared to gate valves.
Common in cooling water, fuel, and chemical systems.
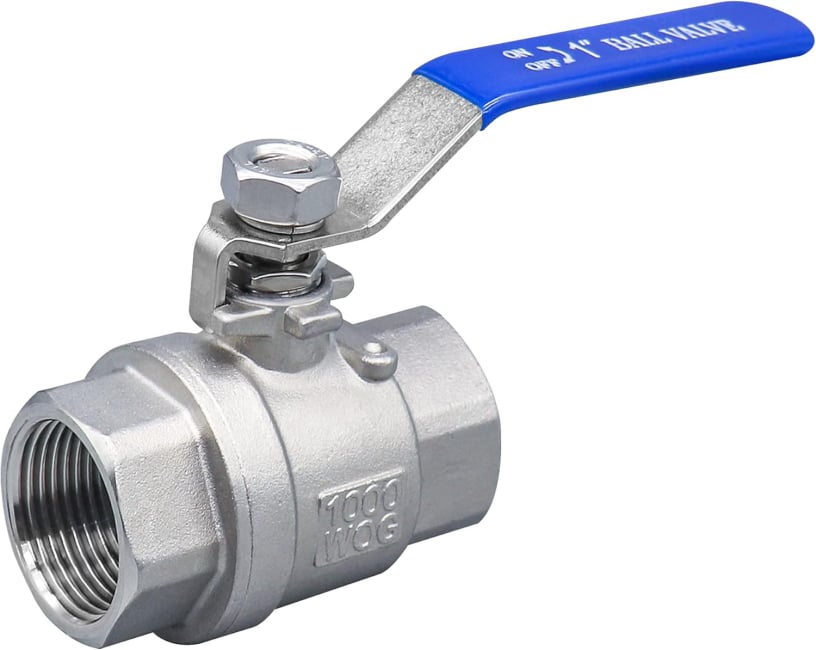

Ball Valve
Function: Quick shutoff, quarter-turn operation (90°).
Uses a spherical ball with a hole through it.
Provides tight sealing, easy operation.
Common in gas lines, water systems, and compressed air.
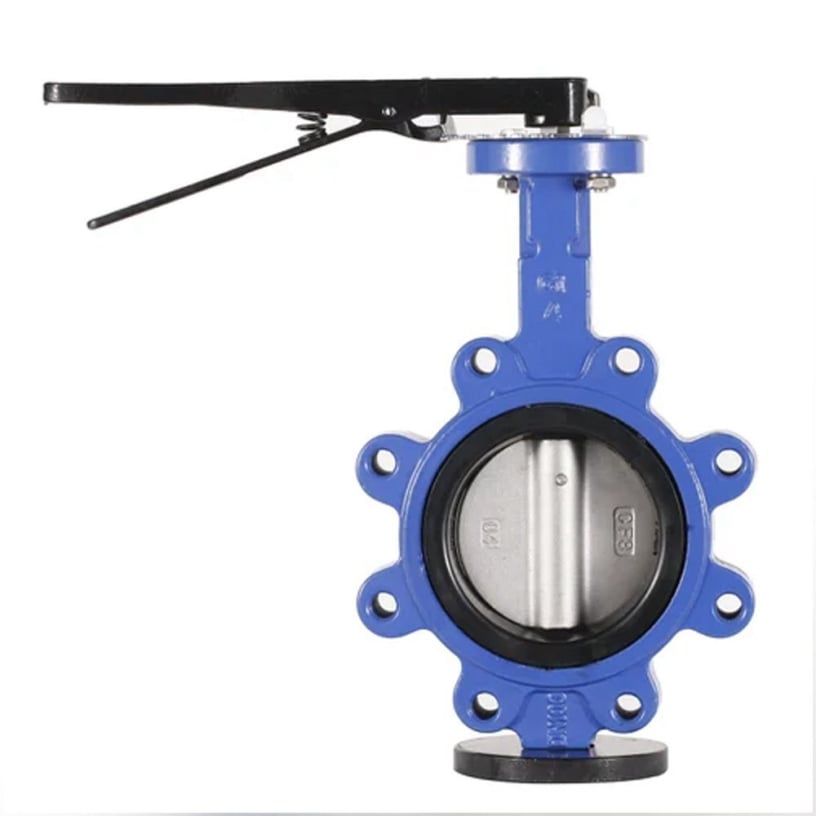

Butterfly Valve
Function: Used for on/off and throttling.
Has a disc that rotates (quarter-turn) inside the pipe.
Lightweight, compact, and cost-effective.
Common in water supply, HVAC, and fire protection.
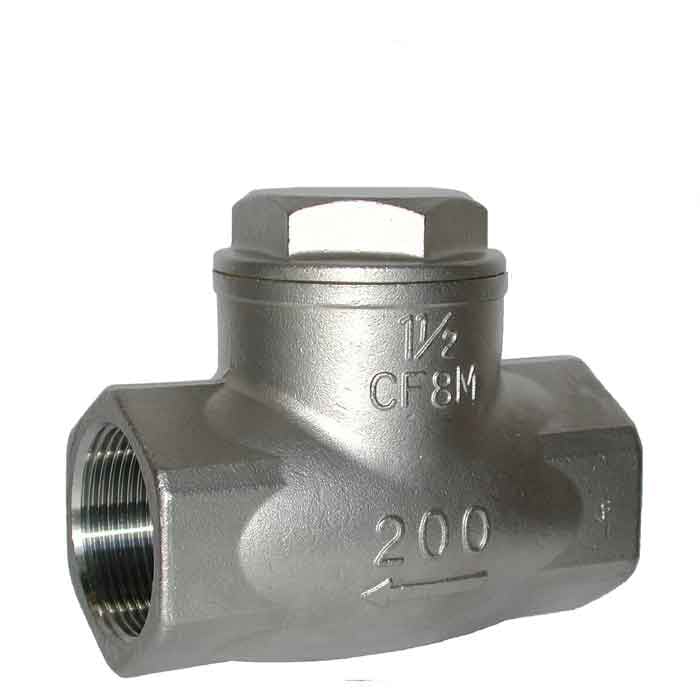

Check Valve (Non-Return Valve)
Function: Allows flow in one direction only (prevents backflow).
Operates automatically (no hand operation).
Common in pumps, water systems, and compressors.
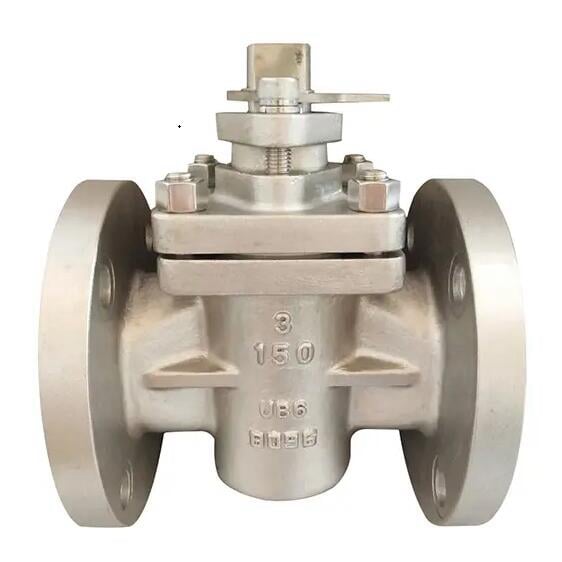

Plug Valve
Function: Similar to ball valve, quarter-turn operation.
Uses a cylindrical or conical plug with a hole.
Good for quick operation but less efficient for throttling.

Diaphragm Valve
Function: Uses a flexible diaphragm to control flow.
Suitable for corrosive and slurry fluids.
Common in chemical and pharmaceutical industries.

Pressure Relief (Safety) Valve
Function: Automatically releases pressure when it exceeds a set limit.
Essential for boilers, compressors, and pressure vessels.
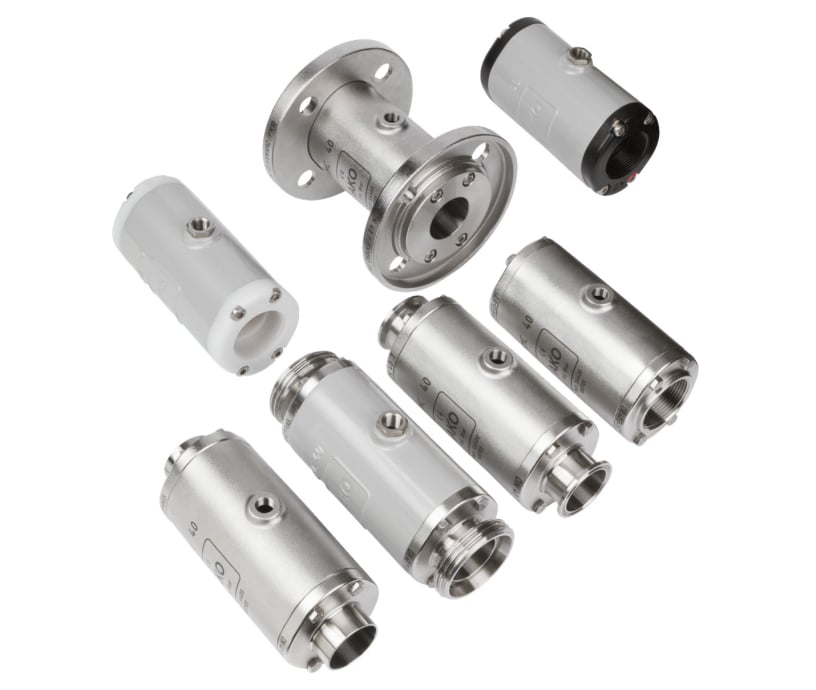

Pinch Valve
Function: Uses a pinching mechanism on a flexible tube to stop/allow flow.
Excellent for slurries, corrosive, and abrasive fluids.
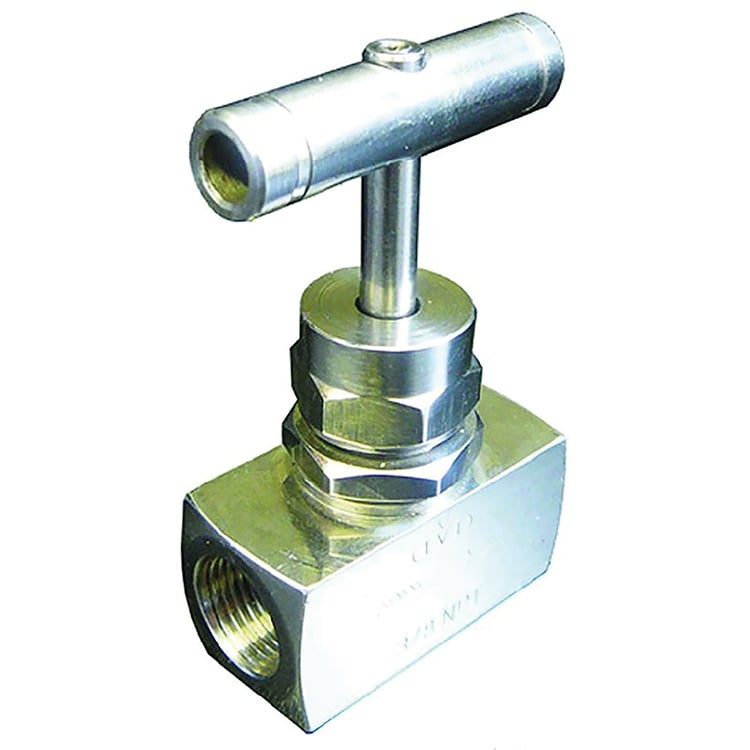

Needle Valve
Function: Used for precise flow control (fine adjustments).
Small size, common in instrumentation and fuel systems.