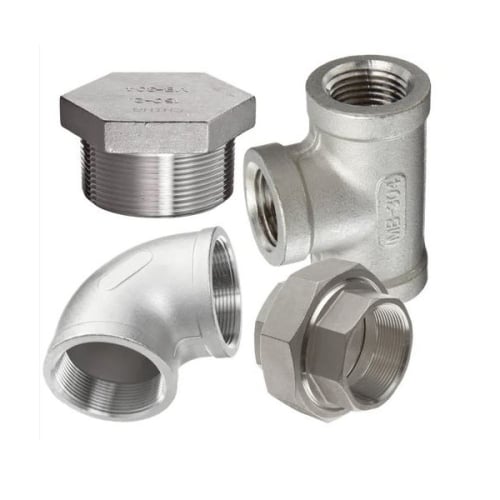
Common Types of Pipe Fittings
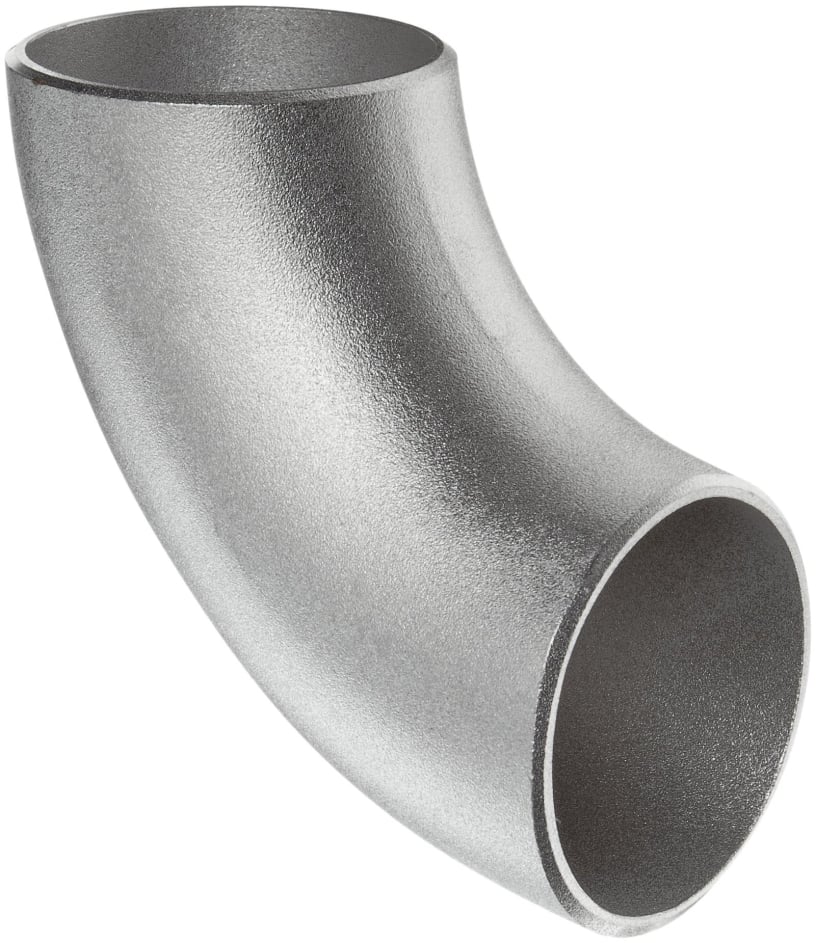

Elbow
Used to change the direction of flow.
Common angles: 45°, 90°, 180°.
Available as short-radius and long-radius types.
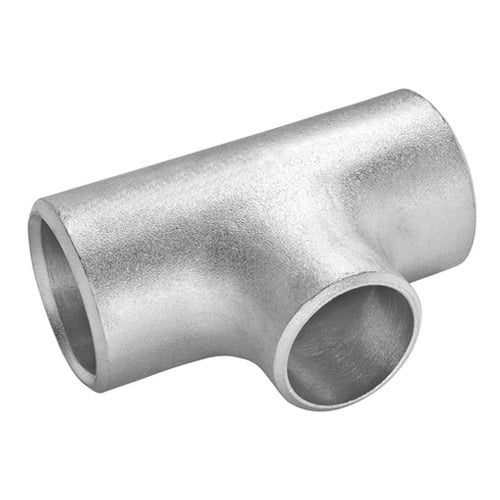

Tee
Has one inlet and two outlets (T-shape).
Used to branch the pipeline.
Types: Equal Tee (all openings same size), Reducing Tee (one outlet smaller).

Reducer
Connects pipes of different diameters.
Concentric Reducer: Centerlines of pipes are the same.
Eccentric Reducer: Centerlines are offset (to prevent air pockets in horizontal pipes).

Coupling
Used to join two pipes together.
Types: Full Coupling, Half Coupling, Reducing Coupling.
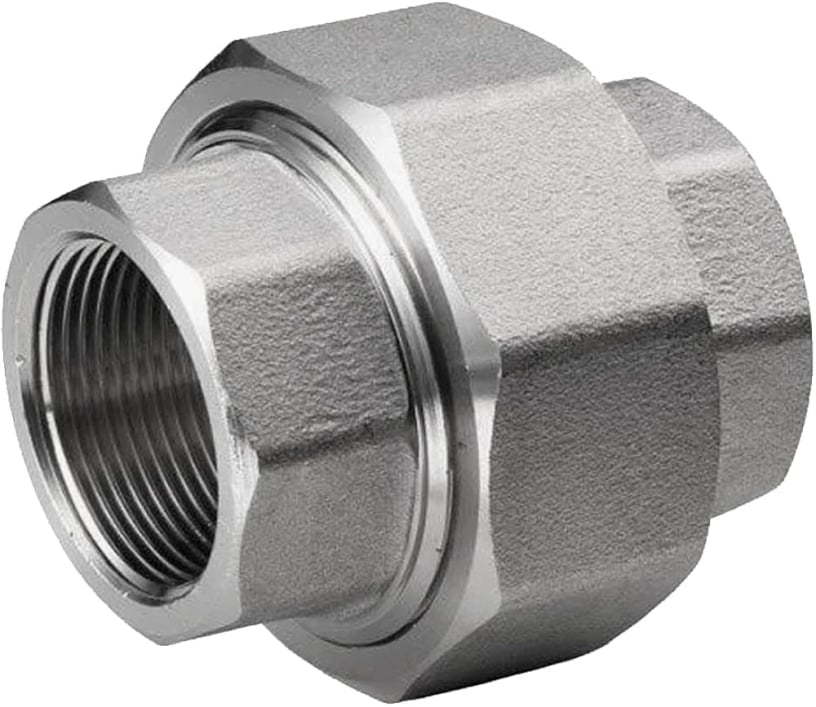

Union
Similar to a coupling but allows quick disconnection (maintenance-friendly).

Cross (Four-way fitting)
Has one inlet and three outlets (like a “+”).
Used in fire-fighting systems, sprinklers, and irrigation.
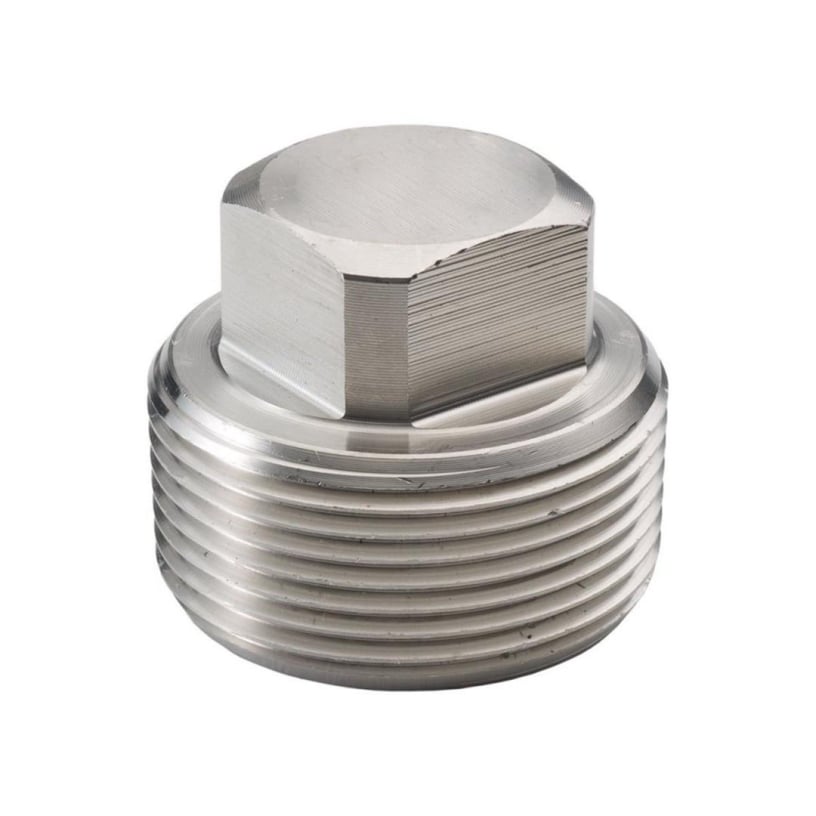

Cap / Plug
Used to close or terminate the end of a pipe.
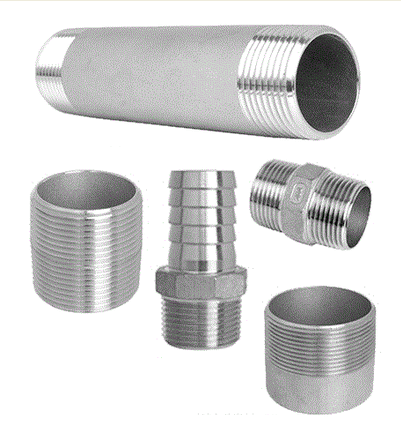
Nipple
Short length of pipe with male threads on both ends.
Used for small-length connections.
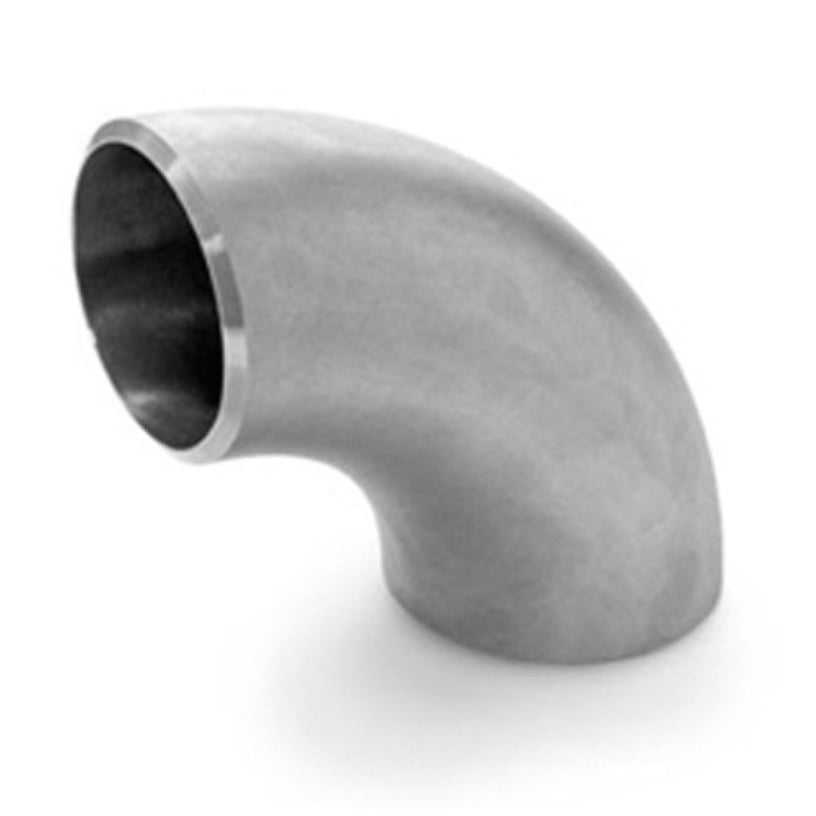

Bend
Like an elbow but has a larger radius for smooth flow (less pressure drop).

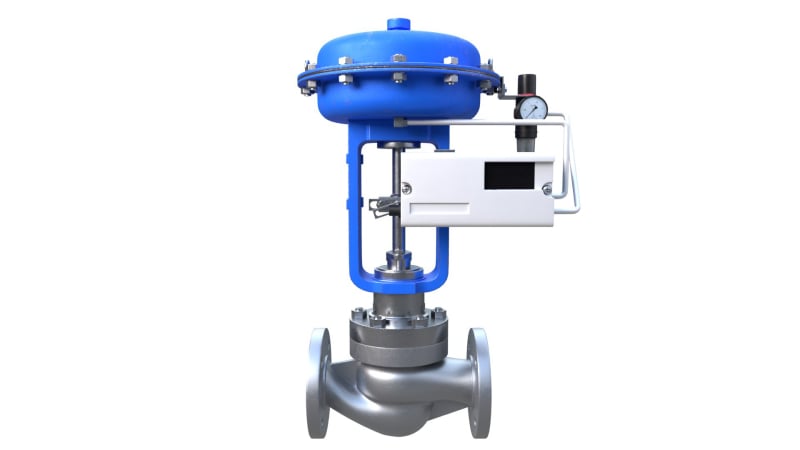
Valve (Technically a fitting)
Controls the flow of liquid/gas.
Types: Gate Valve, Ball Valve, Globe Valve, Butterfly Valve, Check Valve.