Types of Structural Material

Metals
Steel
Strong, tough, ductile.
Widely used in construction (beams, columns, pipelines, bridges).
Types: Carbon steel, Alloy steel, Stainless steel.
Aluminum
Lightweight, corrosion-resistant.
Used in aircraft, ships, and lightweight structures.
Cast Iron
Brittle but good in compression.
Used in pipes, machine bases, and manholes.
Copper & Alloys (Brass, Bronze)
High corrosion resistance, electrical/thermal conductivity.
Used in roofing, plumbing, and electrical systems.
Concrete & Masonry
Reinforced Concrete (RCC)
Concrete + steel reinforcement → high strength in compression and tension.
Used in bridges, buildings, dams.
Pre-stressed Concrete
Steel tendons placed under tension before loading.
Used in long-span bridges and heavy structures.
Brick & Stone
Traditional construction materials.
Good in compression but weak in tension.
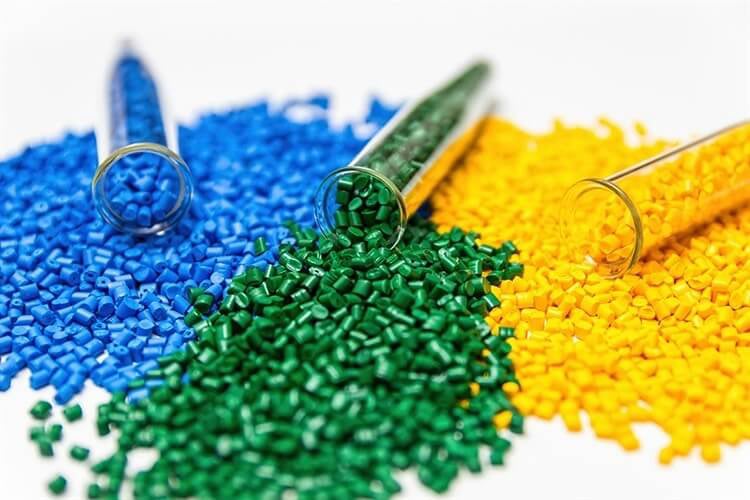

Polymers (Plastics)
PVC, HDPE, Polypropylene
Lightweight, corrosion-resistant.
Used in piping, roofing sheets, and insulation.
Composites (FRP – Fiber Reinforced Plastic)
Strong, lightweight, chemical-resistant.
Used in aerospace, chemical plants, and modern construction.
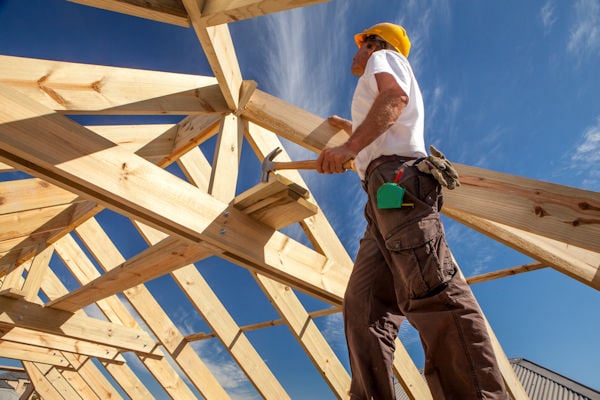

Timber (Wood)
Naturally available, easy to work with.
Used in housing, furniture, and flooring.
Modern engineered wood (plywood, MDF, LVL) improves strength and durability.

Advanced Materials
Ceramics
High heat resistance, used in furnaces and tiles.
Glass
Transparent, brittle, used in buildings and facades.
Nanomaterials & Smart Materials
Emerging structural materials for aerospace and high-tech construction.