Types of Gland Packing Material
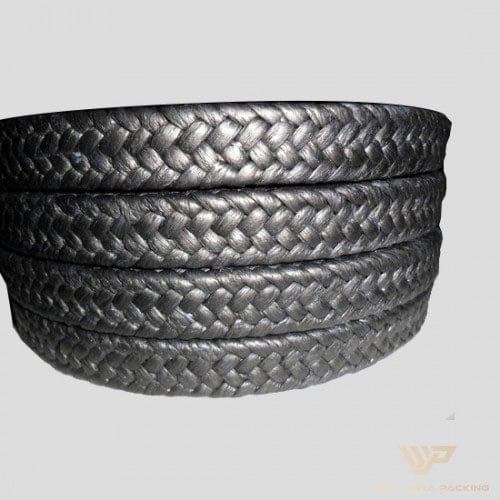

Asbestos Packing
Made from asbestos fibers, sometimes impregnated with lubricants or graphite.
Good heat resistance, but rarely used now because asbestos is hazardous.

Graphite Packing
Made from flexible or braided graphite.
Excellent heat resistance (up to 450–650 °C).
Chemically resistant → used in high-temperature, high-pressure steam, and chemical services.
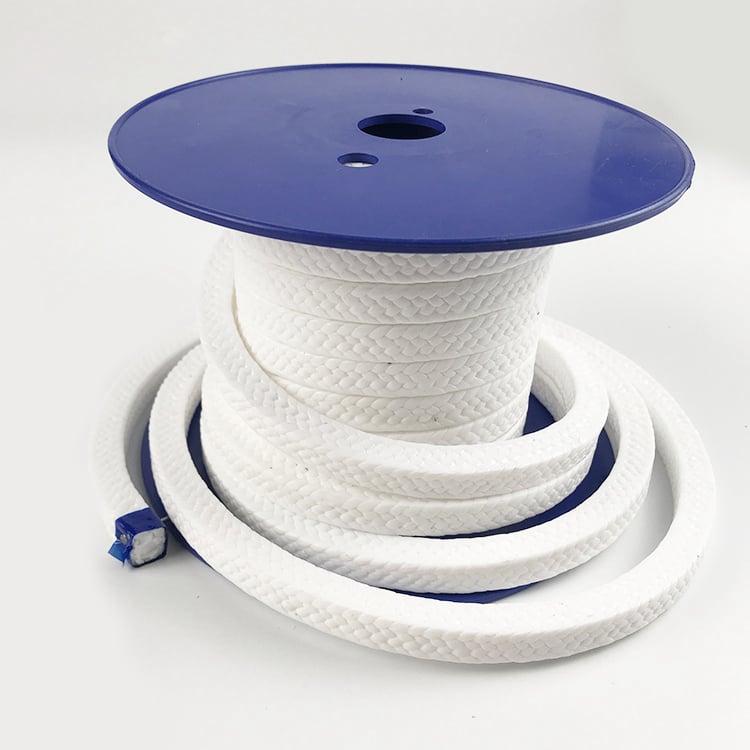

PTFE (Teflon) Packing
Made from Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE).
Excellent chemical resistance and low friction.
Suitable for corrosive fluids but not for very high temperatures.
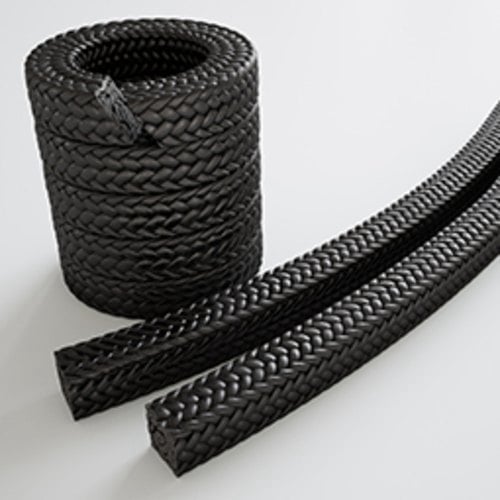

Carbon Fiber Packing
Braided carbon fiber, sometimes with graphite.
High strength, good thermal conductivity, and chemical resistance.
Used in pumps and valves for chemicals, steam, and hot water.
Metallic Packing
Made from soft metals like lead, aluminum, or copper.
Can withstand very high pressure and temperature.
Rarely used today, replaced by graphite and advanced composites.
Non-Asbestos Fiber Packing
Made from synthetic fibers (aramid, acrylic, Kevlar®) with lubricants.
Environmentally safe alternative to asbestos.
Used in general service applications.