Type of Flanges
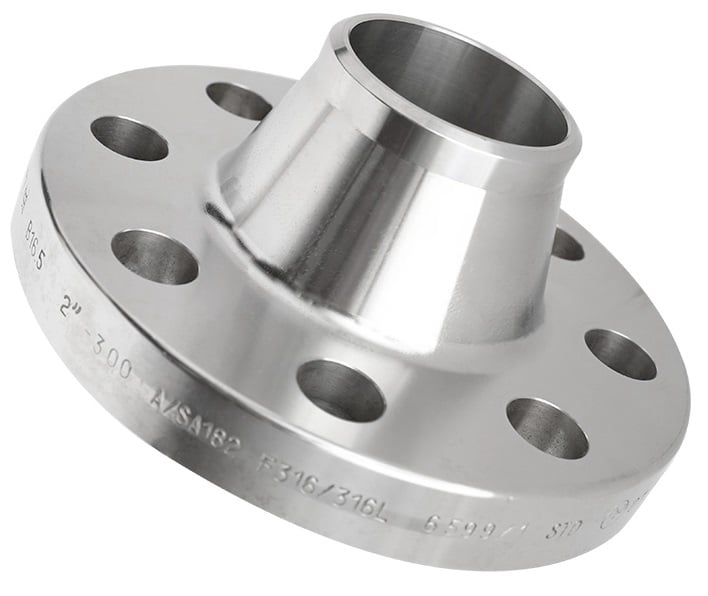

Weld Neck Flange
Has a long tapered hub.
Welded to the pipe at the neck for high strength and smooth flow.
Best for high-pressure and high-temperature applications.
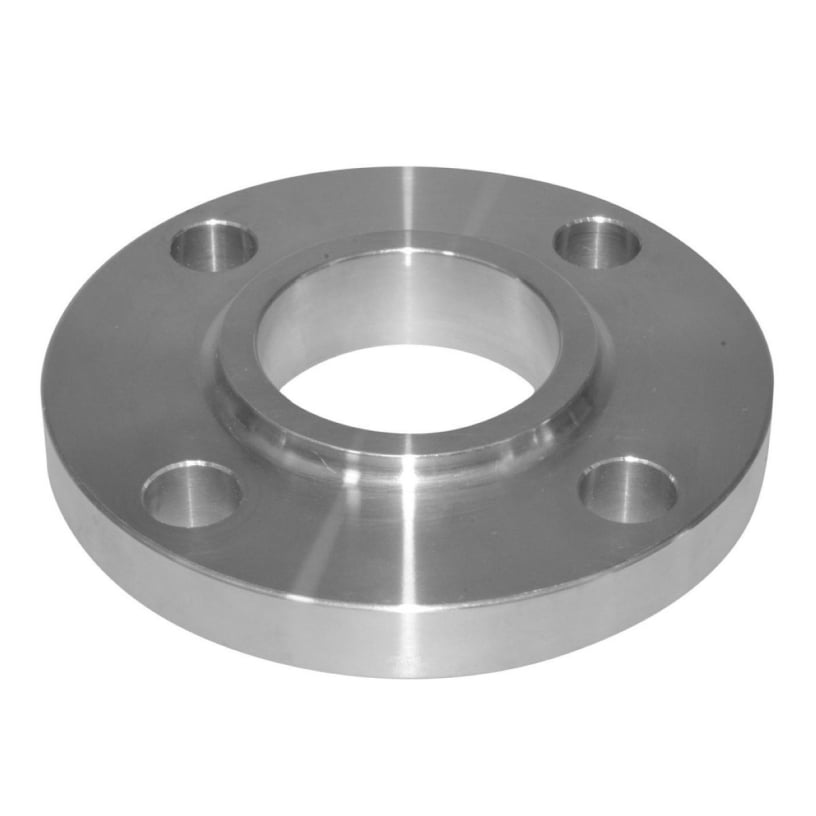

Slip-On Flange
Pipe is inserted into the flange before welding.
Easier to align than weld neck but not as strong.
Common in low-pressure piping.
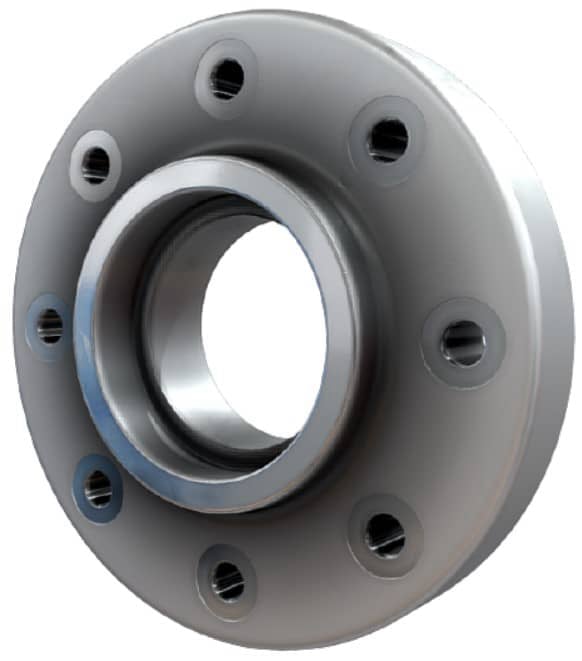

Socket Weld Flange
Pipe is inserted into a socket inside the flange and fillet welded.
Provides good strength but mainly for small-diameter, high-pressure pipes.
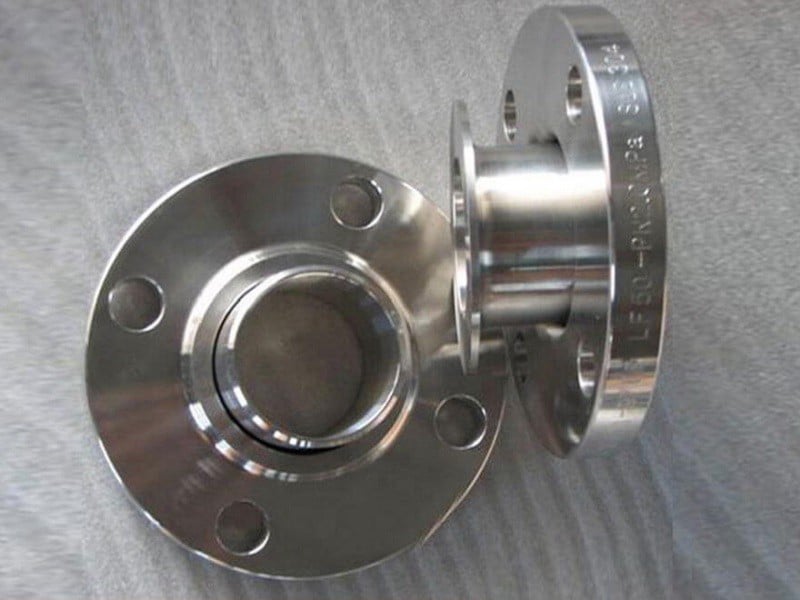

Lap Joint Flange
Used with a stub end.
The flange itself does not contact the fluid.
Allows easy dismantling → ideal for systems that need frequent inspection/cleaning.
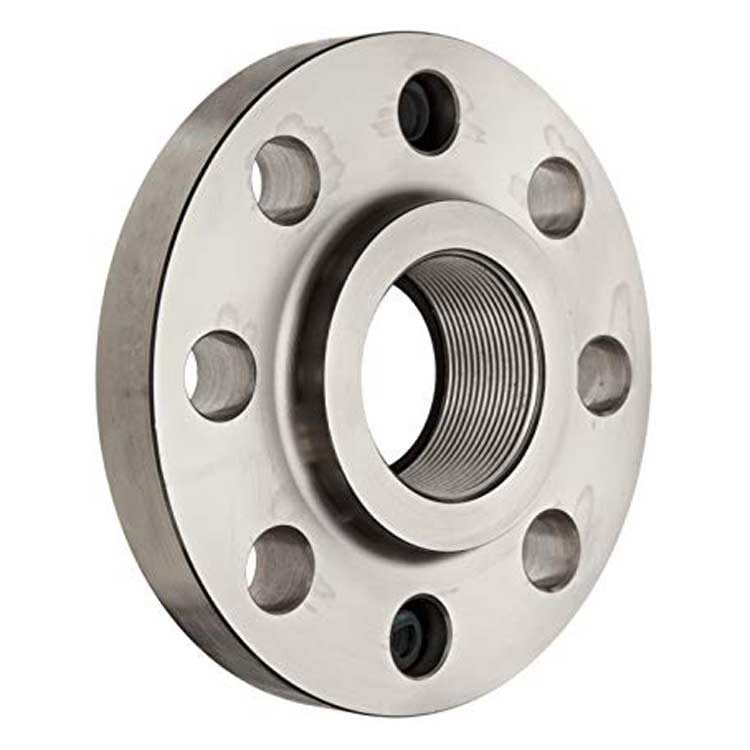

Threaded (Screwed) Flange
Connected to the pipe using threads (no welding needed). Suitable for low-pressure and non-critical applications.
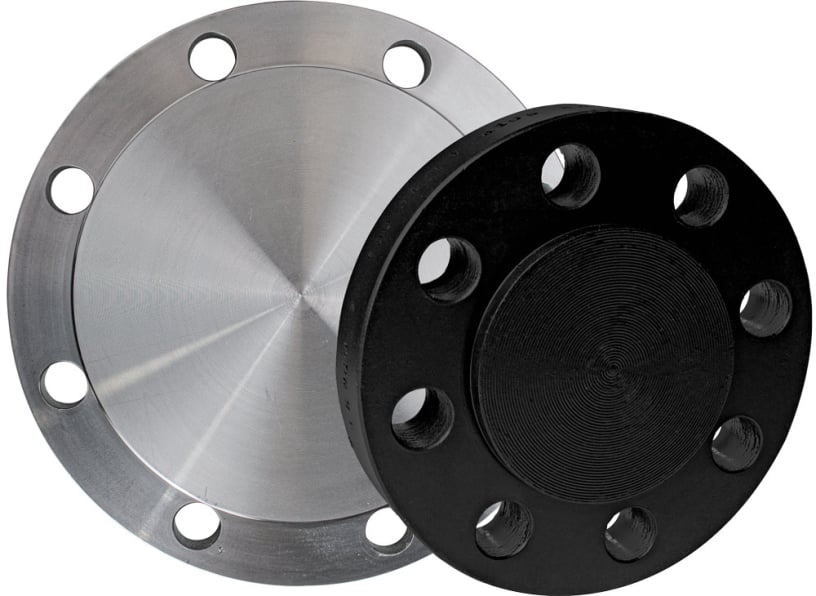

Blind Flange
A solid disk used to close the end of a pipe or nozzle. Provides access for inspection/maintenance. Withstands high pressure.
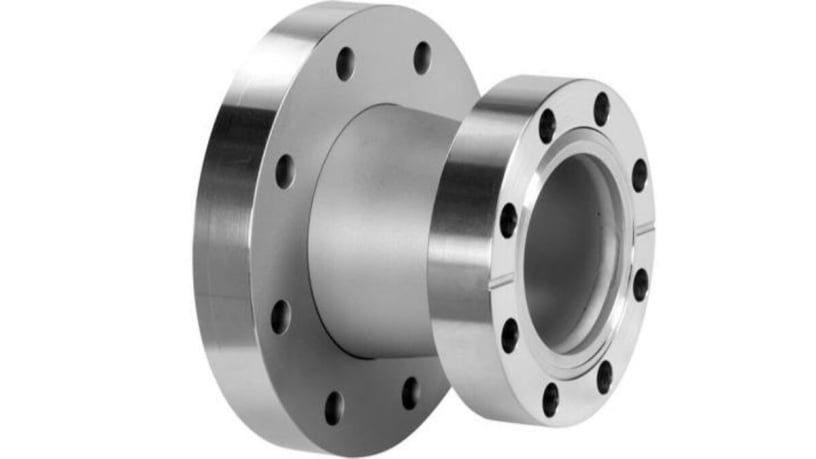

Reducing Flange
Used to connect different pipe sizes. Acts as a flange and reducer in one piece.
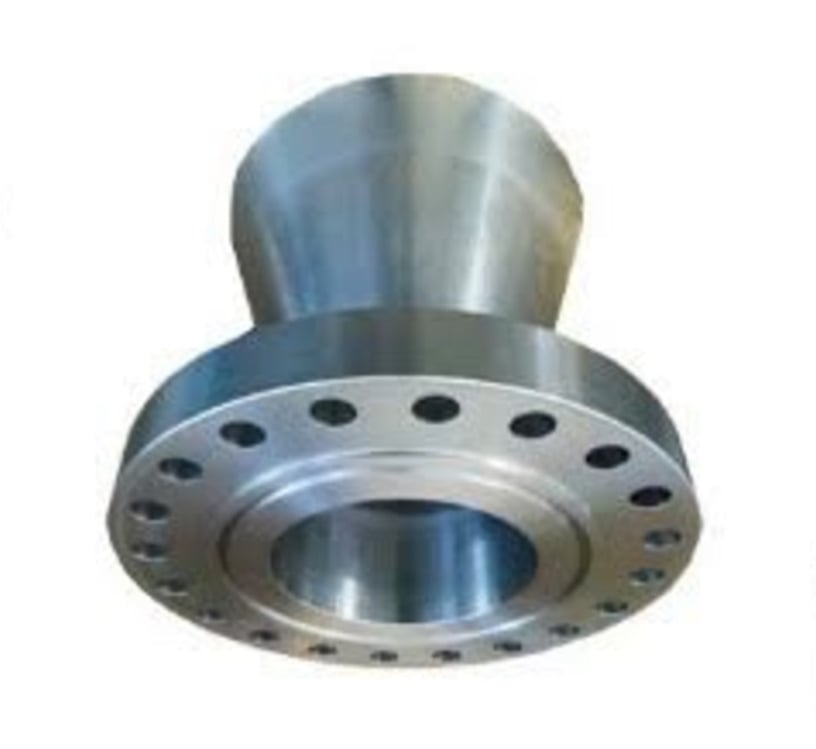

Expander Flange
Increases pipe bore size (opposite of reducing flange). Useful when pipe size changes at equipment connections.

Orifice Flange
Has holes for orifice plates and pressure taps. Used for measuring flow rate of fluids.
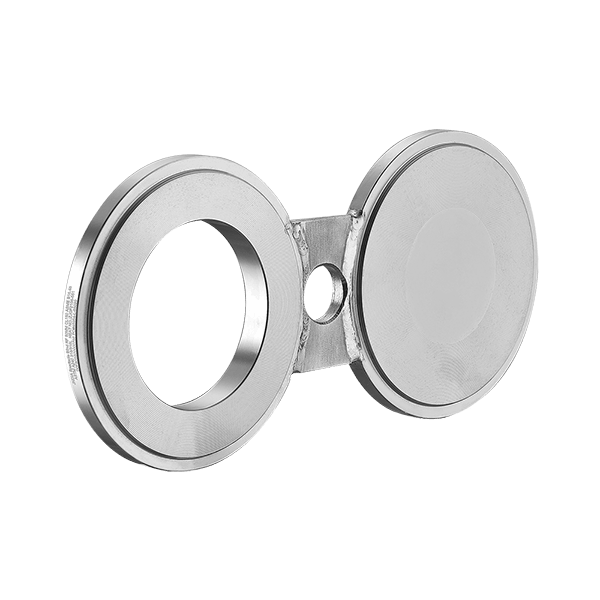

Spectacle Blind Flange
A pair of flanges shaped like spectacles (one open, one closed). Used in pipelines where flow needs to be periodically stopped.
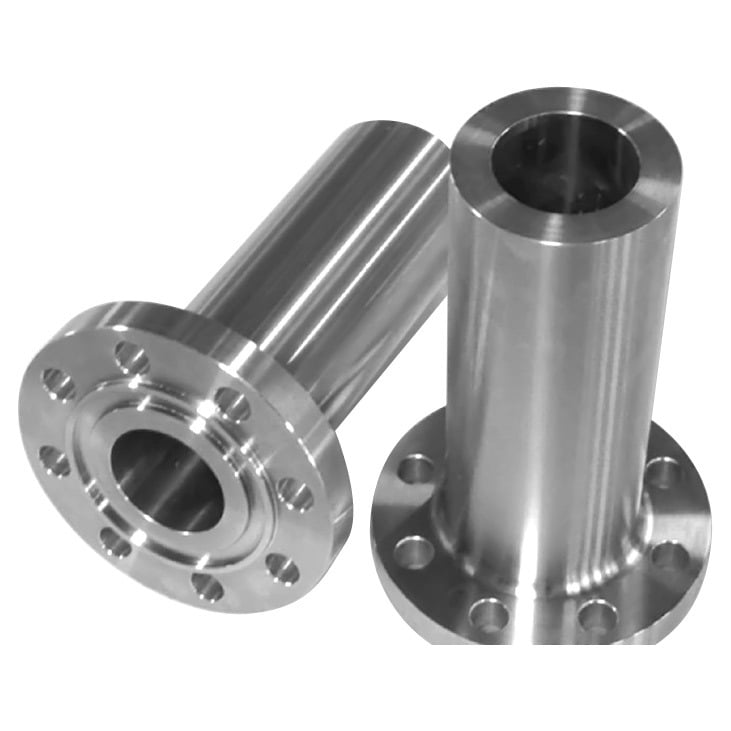

Long Weld Neck Flange
Similar to weld neck but with a longer hub. Often used in vessels, columns, and high-pressure equipment.