Main Categories

Material Handling Equipment
Used to move, lift, and store materials.
Examples: Cranes, Forklifts, Conveyors, Hoists, Elevators.

Manufacturing & Production Equipment
Machines that shape, cut, or assemble products.
Examples: Lathes, Milling machines, CNC machines, Welding machines, Injection molding machines.
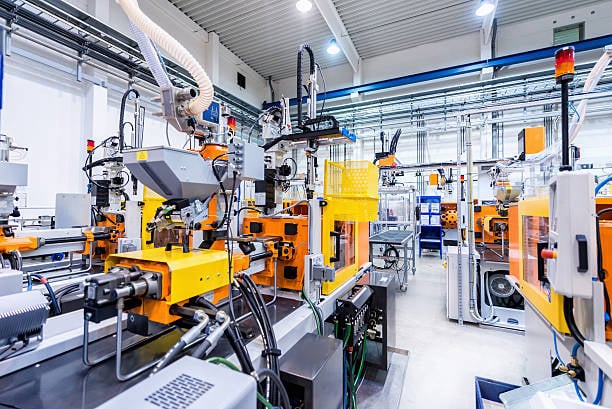

Process Equipment
Used in industries like chemical, oil & gas, food processing, and pharmaceuticals.
Examples: Boilers, Heat exchangers, Reactors, Distillation columns, Evaporators, Pumps, Compressors.
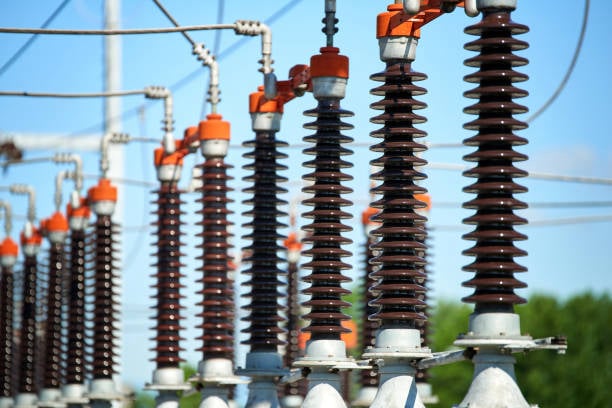

Power & Utility Equipment
Provides power, heating, cooling, and compressed air to industries.
Examples: Generators, Turbines, Chillers, Air compressors.
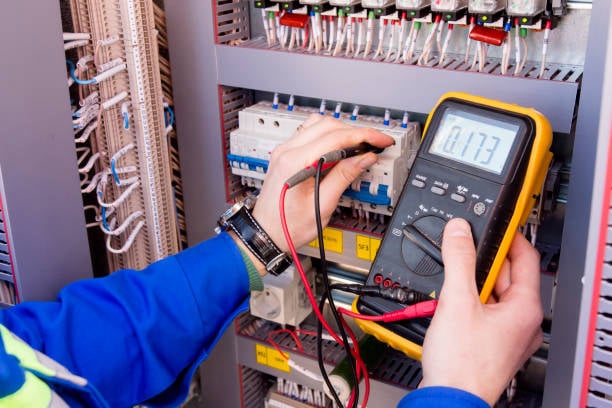

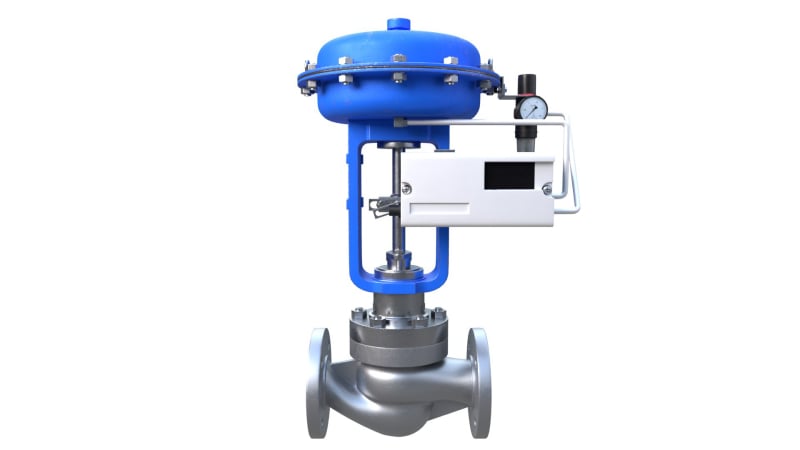
Measurement & Control Equipment
Monitors and controls industrial processes.
Examples: Pressure gauges, Flow meters, Control valves, Sensors, PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers).
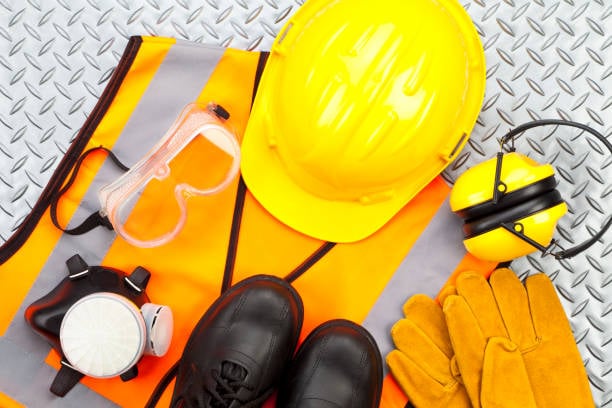

Safety Equipment
Protects workers and machinery.
Examples: Fire extinguishers, Safety alarms, PPE (helmets, gloves, goggles), Emergency showers.

Packaging Equipment
Used to pack and label products.
Examples: Wrapping machines, Labeling machines, Sealing machines.