Products

Pipe
A pipe is a tubular section or hollow cylinder, usually made from metals, plastics, concrete, or ceramics, that is used primarily to convey substances such as liquids, gases, or sometimes solid particles in slurry form. Pipes are essential components in water supply systems, oil and gas industries, chemical plants, HVAC systems, and domestic plumbing.
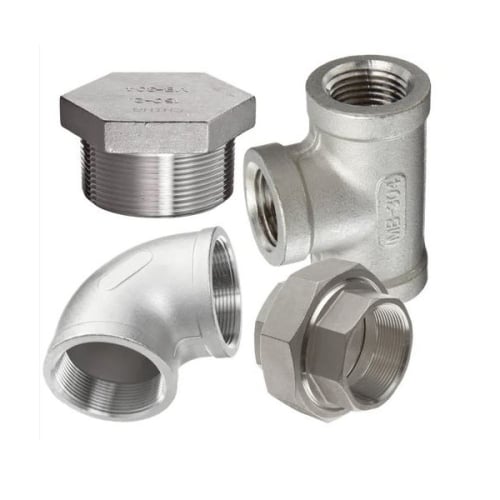

Pipe Fittings
Pipe fittings are components used to connect, control, or terminate the flow in piping systems. They allow pipes to change direction, branch off, increase/decrease in size, or connect different materials.
They are made from materials such as steel, copper, brass, PVC, CPVC, HDPE, and cast iron, depending on the application (plumbing, oil & gas, irrigation, HVAC, etc.).

Flanges
A flange is a mechanical device used to connect pipes, valves, pumps, and other equipment in a piping system. It provides strength, easy assembly/disassembly, and access for inspection, cleaning, or modification. Flanges are usually joined by bolting and sealed with a gasket.

Valves
Valves are mechanical devices used in piping systems to start, stop, regulate, or direct the flow of fluids (liquid, gas, or slurry).
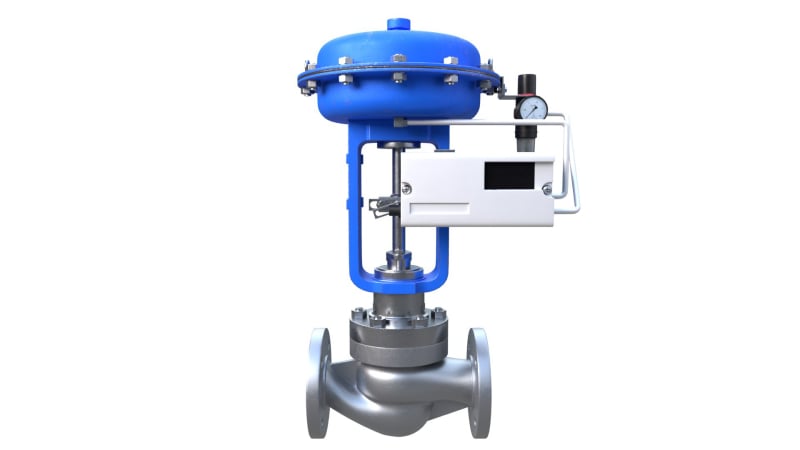

Control Valves
A control valve is a type of valve used to regulate the flow rate, pressure, temperature, or liquid level in a piping system by varying the size of the flow passage. Unlike simple on/off valves (like gate or ball valves), a control valve works automatically it receives a signal from a controller and adjusts its opening to maintain the desired process condition.

Packing Material
Packing material is a sealing element used inside valves, pumps, and piping equipment to prevent fluid leakage along the moving parts (such as valve stems or pump shafts). It fills the space between the valve stem/shaft and the bonnet or stuffing box to form a tight seal, while still allowing movement.

Structure Material
A structural material is any material that is used to bear loads, provide strength, and ensure stability in structures like buildings, bridges, machines, pipelines, ships, and vehicles. The choice of material depends on strength, durability, weight, corrosion resistance, cost, and environmental factors.
Gauges
A gauge is an instrument used to measure, indicate, or compare a physical quantity such as pressure, level, thickness, or diameter.
In engineering and manufacturing, gauges help ensure accuracy, safety, and quality control.